-
Custom Gearbox Design Process
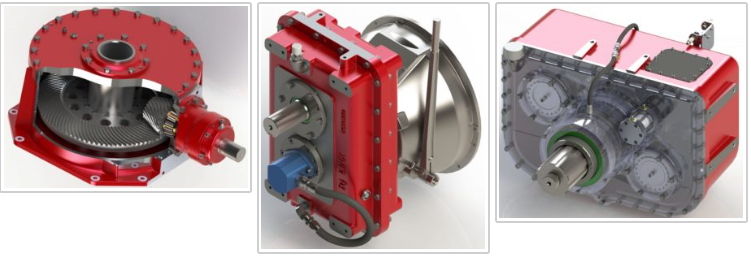
Rj Link Custom Gearbox Design Process
Some of the unique features that are reviewed in the Rj Link process:
- Advanced design methodology for custom gearboxes
- Improved surface finish with formed tooth grinding & dressable wheels
- Material cleanliness
- Housing is designed for rotor stability and noise reduction
- Superior bearing design
- Customer interface with 3D design technology
- Gearing system is designed using FEA capabilities for gear teeth and castings
Once the above features are reviewed with the customer, the Rj Link engineering team starts looking at specifications, ratings and cost. A decision has to be made on rating to AGMA, API or another standards. Some of the requirements that Rj Link looks at for comparison are design & features, quality assurance and testing.
Comparing AGMA vs. API:
Some of the basic requirements that cover AGMA and API standards are the gear rating and service life. It’s the gear element construction and quality that matters to us. We get into dynamics, worry about vibration, bearings, noise, lube system, base plates, testing & QA documentation.
- AGMA – Low speed and high speed gearboxes. We rate AGMA 6011-6013.
- API – Rated to 677 general purpose and 613 special purpose. 613 refers to lower speed boxes, low power, and non-crucial applications. When talking about critical applications, or special purpose gearboxes, this is considered much higher speed, higher power, etc.
Other specifications in special gear units are the load capacity calculations, especially for spurs and helicals. We go back and do a comparison to an AGMA 2001-C95 standard.
Ratings: Looking at durability and strength.
Durability: API is a stringent rating system with no room for variation.
Strength: This is the bending stress number. This lets us know how much load can be put on the teeth before they flex and get into their elastic range.
Other Criteria:
- Ratio of the face width to the pinion pitch diameter.
- Scuffing and method of assess and risk.
- Service factors on high HP/Speed applications.
Cost: There is approximately a 65% increase if you rate something to an API standard. The advantage is that you gain about 5x the design/theoretical service life.
Things to remember that affect the design process:
- Be aware of the specification
- Level of compliance
- Rating on the driven plus the drive in members SF
Necessary information to supply to the gear manufacturer:
- Operating conditions – Need to know the power, speeds, ratio, service factor, duty cycle, type of equipment on the driven side, motor service factor, and if a retrofit or replacement unit need the size, model number, serial number to get the correct footprint.
- Location of installation
- Special testing
- Keyway
- Certifications
- Any required analysis
- Any input, out put coupling, guard modification or adaptors
- Auxiliaries – instrumentation, lube system, base plate, couplings, etc.
- Shaft arrangement & rotation


 1-815-874-8110
1-815-874-8110