-
Helical Gearing Pumping Units
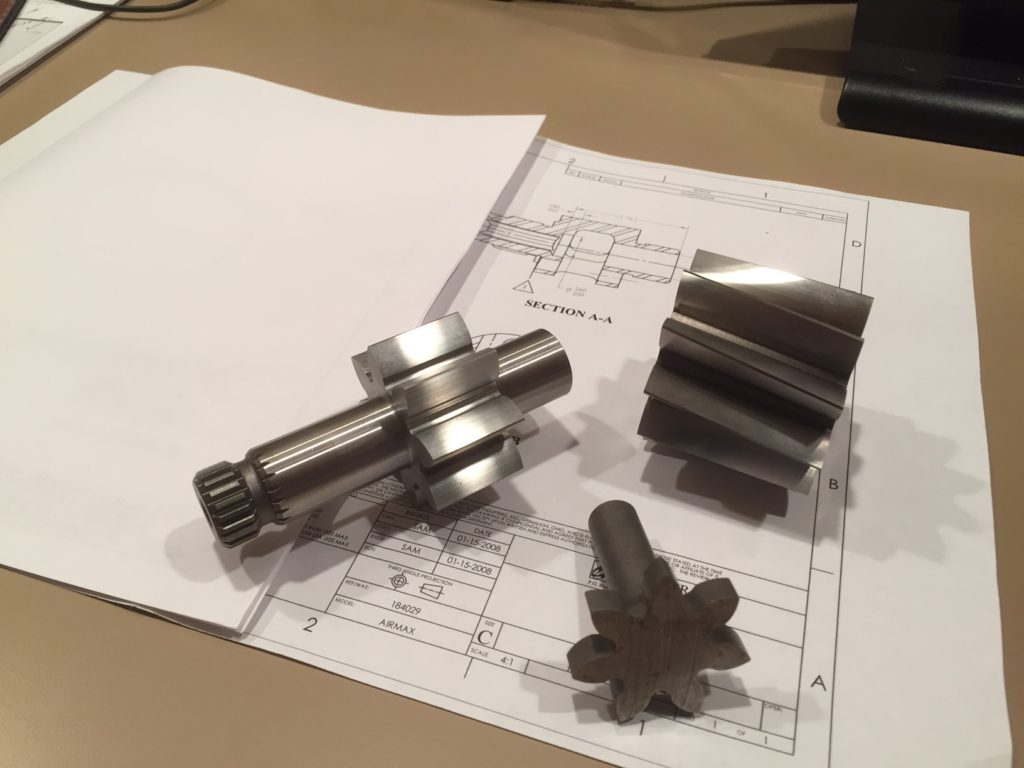
Helical Gearing Pumping Units
Why are helical gears a suitable alternative, and a basis to several of the pumping technologies? One reason is due to the cavity that’s formed with the gear mesh as it rotates within the housing, and the way the media is trapped between the gear mesh. One of the big advantages of a helical gear pump is that it can handle a very wide range of applications, such as shear sensitivity, abrasive slurries, ie. solids, liquids and gas mixtures in some cases.
ELEMENTS TO CONSIDER WITH THESE TYPES OF SYSTEMS:
Gear mesh:
Tooth curvature and enhanced profile fitting along the minor/major diameter versus the diameter of the housing. What we are trying to calculate is a constant swept volume per revolution. Basically a gear mesh capacity (flow rate). Another key in the design of the gear set and gear pump is internal leakage/slip within the system. We want to control minimal slippage over the gear teeth. The goal is to avoid backward flow/pressure. Keeping in mind, this is a positive displacement type system.
Housing:
It’s important to build a uniform thickness throughout the housing. This thicker housing is less prone to distortion, and therefore will help stabilize the unit and hold the pressure in better.
The following are some of the enhanced operating characteristics we consider when designing this type of system:
- Good suction capability
- Good wear characteristics
- Optimal solid handling
- Reduced vibration
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS:
Abrasives – Mining and minerals, certain ceramics, cement, clay, etc.
Sludges – Sewage
Viscous – adhesives, etc.
Shear sensitive – Latexes, cosmetics, dairy type products, etc.
Solids in suspension – Drill cuttings, food type products
Multi-phase liquids– Crude and waste types


 1-815-874-8110
1-815-874-8110